Vietnam’s Coffee Crop Shortfall Could Sustain High Prices
A drought in Vietnam threatens the robusta coffee crop, potentially leading to a 10% shortfall in production this year, which has already driven prices to a near 50-year high. This situation reflects broader climate change impacts on global agriculture and suggests increased volatility in food prices, raising concerns about inflation and investment opportunities in agricultural technology.
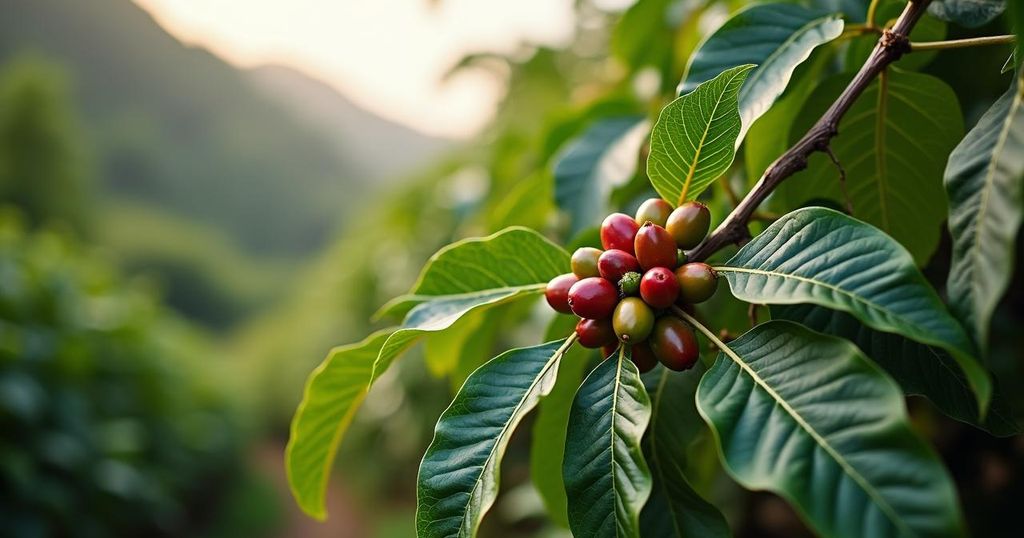
Vietnam is facing a significant impact on its robusta coffee bean production due to a severe drought, marking the worst in a decade. The nation ranks as the world’s second-largest coffee producer and is the leading cultivator of robusta beans, which are pivotal to many coffee drinks. Experts anticipate that the coffee crop may fall short of its annual target by as much as 10%. This anticipated shortfall has already led to a spike in robusta futures, which have reached their highest levels in nearly 50 years. Compounding the issue, Brazil has also experienced a frost affecting its arabica bean production, thereby escalating coffee prices globally and contributing to ongoing coffee shortages for the third consecutive year.
The coffee market is currently under strain due in large part to natural climate disruptions exacerbated by climate change. Vietnam’s drought exemplifies the broader implications of climate fluctuations, which influence agricultural production and thus contribute to rising food prices and inflation. Additionally, the correlation between climate change and agricultural yields suggests that economic repercussions could be significant, potentially leading to global inflation increases exceeding 1 percentage point annually by the year 2035. Central banks have historically overlooked food prices in their inflation metrics, posing challenges for economic policy in response to food price volatility. Furthermore, these challenges present opportunities for investment in agricultural technology aimed at increasing productivity and sustainability in food production.
In summary, Vietnam’s coffee crop shortfall due to drought conditions is poised to maintain high coffee prices, underscoring the interconnectedness of climate change and agricultural productivity. With the potential for continued volatility in food prices driven by climatic events, stakeholders must consider both the economic implications and the opportunities that may arise in agricultural technology sectors aimed at enhancing farm outputs. The ongoing situation emphasizes the critical nature of adaptive measures in agriculture to mitigate the impacts of climatic variability on food security and economic stability.
Original Source: finimize.com



Post Comment