Impact of the 2023/2024 El Niño Event: A Global Overview of Challenges
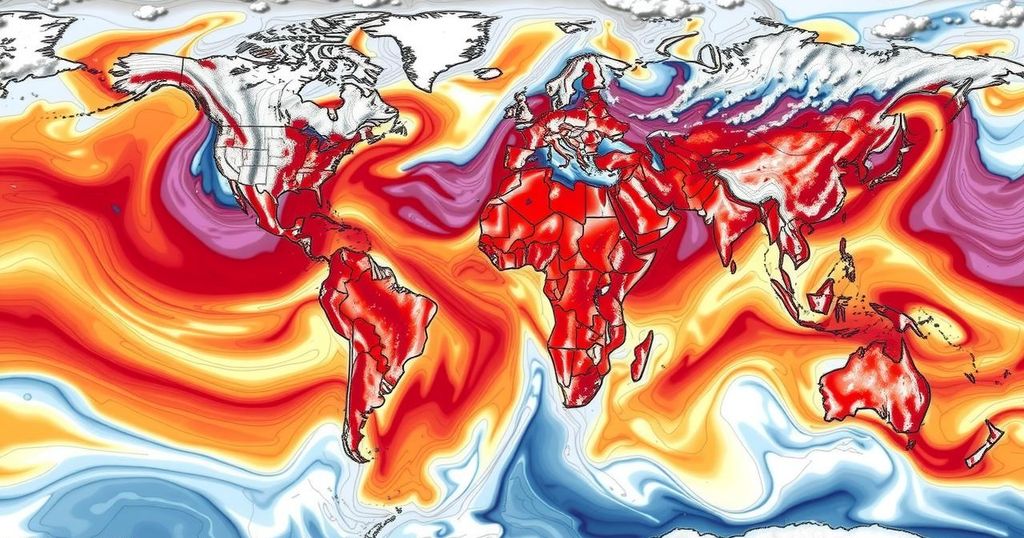
The 2023/2024 El Niño event is among the strongest recorded, causing extreme weather patterns globally, including significant droughts and floods. Over 60 million people have been affected, with severe impacts noted in Southern and Eastern Africa, as well as in Central and South America. This climatic phenomenon has exacerbated food insecurity and health crises, leading to an increase in diseases and risks for vulnerable populations such as women and children.
The El Niño phenomenon for the 2023/2024 period has emerged as one of the most potent episodes recorded, showcasing temperature anomalies exceeding 2°C above average in the Pacific Ocean. This climatic event has primarily influenced an array of extreme weather situations from September 2023 to May 2024. According to the World Weather Attribution organization, the impacts of El Niño manifest starkly across various regions, with a notable prevalence of drought conditions affecting Central America, Colombia, and several nations in Southern Africa, such as Angola and Zimbabwe, where severe effects are ongoing.
In parallel, widespread flooding events have been documented in countries including Brazil, Dubai, Oman, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and regions within East Africa, illustrating the expansive reach of El Niño’s consequences. More than 60 million individuals have been impacted, notably marginalized communities facing the dual threats of climate change and socio-economic instability. The dire conditions in Southern Africa, where over 30 million individuals are grappling with severe drought, have resulted in significant disruptions to food security and livelihoods.
Moreover, the flooding in Eastern Africa has displaced numerous communities and devastated local economies, with around 5 million people affected by these incidents. In the Philippines, over 4 million individuals are enduring drought conditions, while Central America sees approximately 1.3 million impacted by these climatic fluctuations. Brazil alone reports over 2 million residents facing catastrophic flooding.
Beyond food insecurity, the ramifications of El Niño are broad, exacerbating public health crises with rising incidences of diseases such as cholera and malaria in afflicted areas. Vulnerable populations, particularly women and children, face increased risks associated with displacement, economic hardship, and gender-based violence, further destabilizing their living conditions. The far-reaching economic repercussions of these climatic events have disrupted livelihoods and threatened the foundational integrity of social systems across affected regions.
El Niño, part of the El Niño Southern Oscillation, refers to the periodic warming of ocean surface temperatures in the eastern tropical Pacific. This climatic phenomenon significantly influences global weather patterns, often resulting in extreme weather conditions. The current episode, noted for its intensity, has elicited widespread consequences, particularly in terms of food security, health, and socio-economic stability for vulnerable populations across various regions of the world. As climate change intensifies global weather unpredictability, the impacts of such episodes warrant urgent attention and preparedness.
In summary, the 2023/2024 El Niño phenomenon has precipitated one of the strongest instances of climatic disturbance recorded, profoundly affecting millions worldwide. From extensive droughts to devastating floods, the repercussions have disproportionately impacted vulnerable communities, compounding existing challenges related to food security and public health. Addressing the multifaceted consequences of such climatic events remains a pressing global challenge, requiring coordinated efforts to mitigate future impacts and enhance resilience in the face of ongoing climate change.
Original Source: reliefweb.int



Post Comment